How To Learn Texas Holdem Odds
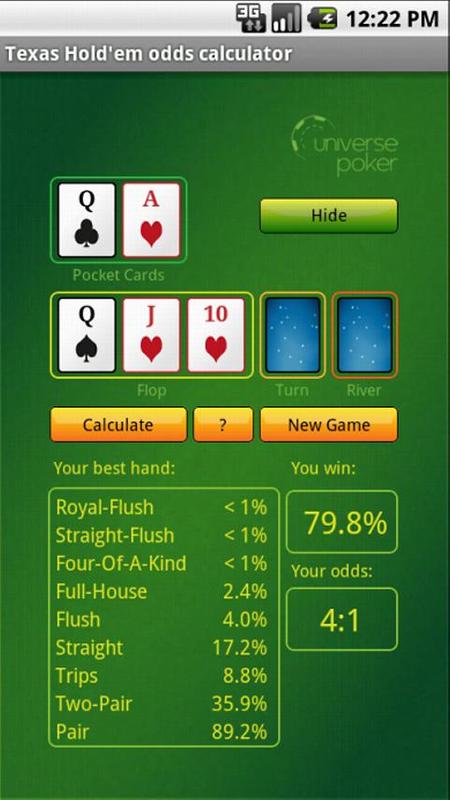
Rough Odds for Texas Hold’em. Playing poker is about playing the odds. The following list gives the odds for outcomes in Texas Hold’em hands. When you realize how heavily the odds are stacked against you, you may want to rethink going all-in before the flop with two suited cards. Calculating pot odds in Omaha is a very similar endeavour to that in Texas Hold’em. The biggest difference, however, concerns the outs: You’re often going to have a lot more of them (outs) to improve your hand (from having multiple two-card hand combinations with your two extra hole cards). Please watch: 'Free Poker Coaching Program - Rounder University' - Poker probability and pot odds are some of.
Is poker a game of skill or chance? This question has been discussed and
argued in many places and is the center of the arguments for and against
legalizing Texas holdem and other forms of poker in many places, including
online.
The answer to this question boils down to the mathematics behind the game. If
the math shows one player can win more often than another based on the
mathematical and statistical truths about Texas holdem then the game is one of
skill.
Let’s look at a few facts before moving on.
- Fact 1
Texas holdem is played with a deck of 52 playing cards, consisting of
the same four suits, and 13 ranks in every deck. You know each deck has an
ace of spades, and ace of hearts, an ace of clubs, and an ace of diamonds.
The same is true for kings, queens, and all of the ranks down through twos. - Fact 2
Over a long period of time each player will play from each position at
the table an equal number of times. In other words, each player will play in
the small blind, the big blind, under the gun, on the button, etc. an equal
number of times as other players. If you take two individual players it
might not be 100% the same, but it’ll be close. When you take thousands of
players and average their times played in each position mathematically they
each play the different positions an equal number of times. - Fact 3
The rules in each game are the same for every player at the table.
- Fact 4
The player that starts the hand with a better two card starting hand
wins the hand more often than the player with a worse hand. This has been
proven by computer simulations that run millions of hands and consider every
possible outcome.
Why Is This Important?
The reason all of this is important to Texas holdem players is that you can
use all of this math to help you win.
Though there are thousands of possibilities on every hand of Texas holdem,
you can use the fact that everything is based on a set of 52 cards to predict
outcomes and possibilities at every stage for every hand.
If you start the hand with two aces as your hole cards, you know that the
remaining 50 cards in the deck only have two aces. The remaining 48 cards
consist of four of each rank below the aces. At the beginning of the hand you
don’t know where any of the other cards are located, but as the hand progresses
you learn where some of them are located.
Continuing with the example, if the flop has an ace and two fours, you hold a
full house. You also know the only hand at this time that can beat you is four
fours. Because two fours are on the flop, the number of times a single opponent
has the other two fours is 1 in 1,326 hands. This is such a small percentage of
the time that you always play the full house in this example as if it’s the best
hand.
How do we know the number of times the opponent has the other two fours?
Because two fours are on the flop, let’s say the four of hearts and the four
of diamonds, so you know that your opponent has to have the four of clubs and
the four of spades. The chances of the first card in their hand being one of
these two cards are two out of 52. If they get one of them as the first card
that leaves the single other card they need out of 51 unseen cards, or one out
of 51.
You multiply two over 52 times one over 51 and this gives us the 1 out of
1,326 hands.
Basic Texas Holdem Math
Some of the math we discuss on this page can be complicated and the truth is
some players won’t be able to use it all. But that doesn’t mean they can’t be
winning Texas holdem players. The math covered in this section forms the
building blocks for the advanced math covered lower on the page.
Every Texas holdem player can use the basic math included in this section,
and if you aren’t using it yet you need to start right away.
Starting Hands
At the most basic level of Texas holdem everything starts with your starting
hand. As we mentioned above, mathematically the player who stars the hand with
the better starting hand wins more than the player with the inferior hand.
This means the first math lesson you need to learn and start using is to play
better starting hand on average than your opponents. While this can get
complicated, especially in games with many multi way pots, you still need to
learn how to play better starting hands.
If you take nothing else from this page, if you simply tighten up your
starting hand selection it’ll immediately improve your results.
Position
It’s difficult to directly relate position to mathematics, but the main thin
to know is the later your position, the better your chances to play in a
positive expectation situation. We’ll discuss expectation in a later section,
but it’s important to understand that having position on an opponent is a strong
advantage that equates to a mathematical advantage over the long run.
Outs
One of the most important skills Texas holdem players need to develop is the
ability to determine the number of outs, or cards remaining in the deck that can
complete the hand they’re drawing to. You use this information to determine your
chances of winning the hand as well as to determine the pot odds. Pot odds are
discussed in the next section, but they show you whether or not a call is
profitable in the long run when an opponent makes a bet.
We can determine how many outs you have because we know what’s in the deck
and what we need to improve our hand. If you have a king, queen, jack, and 10
after the turn you know any of the four aces or four nines complete your
straight.
This means you have eight outs. You’ve seen six cards, so the deck has 46
cards remaining in it. Don’t make the mistake of thinking about the cards that
have been folded or your opponent holds. You haven’t seen these cards so any
unseen card is still considered a possible river card.
In other words, on average, if you play this situation 46 times you’re going
to complete your straight eight times and not complete it 38 times.
You should always consider how many outs you have in every situation while
playing. B knowing your outs you have another piece of information that can help
you make profitable decisions throughout the hand.
Pot Odds
The next question many players ask after they learn how to determine their
out sis how they can use this information to make more money at the table. This
is where pot odds come into play.
Pot odds are simply a ratio or comparison between the money in the pot and
the chances you have of completing your hand. You use this ratio to determine if
a call or fold is the best play based on the information you currently have.
If you consider the example in the last section concerning the straight draw,
you know that the deck holds eight cards that complete your straight and 38
cards that don’t. This creates a ratio of 38 to 8, which reduces to 4.75 to 1.
You reduce by dividing 38 by 8.
The way you use this ratio is by comparing it to the amount of money in the
pot and how much you have to put into the pot. If the pot odds are in your favor
it’s profitable to call and if not you should fold.
If the pot has $100 in it and you have to make a $10 call the pot is offering
10 to 1 odds. You determine this the same way as above, by dividing $100 by $10.
If you’re in the situation described above of drawing to a straight on the
river you can see that a call is correct because the pot is offering 10 to 1 and
you have a 4.75 to 1 chance of winning.
On the other hand of the pot has $100 in it and you have to put $40 in to see
the river the pot is only offering 2.5 to 1 odds and your chances of hitting
your straight are still 4.75 to 1 so you should fold.
Pot odds can get complicated, especially when you start considering how they
work when you’re determining the correct play with both the turn and river to
come.
Fortunately charts are available to quickly check the odds of hitting your
hand based on how many outs you have. We’ve included one next so all you have to
do is determine your outs and compute the odds the pot is offering. Then compare
the two to see if it’s profitable to call or fold.
| Number of Outs | Turn & River Combined | River Only |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 22.26 to 1 | 45 to 1 |
| 2 | 10.9 to 1 | 22 to 1 |
| 3 | 7 to 1 | 14.33 to 1 |
| 4 | 5.06 to 1 | 10.5 to 1 |
| 5 | 3.93 to 1 | 8.2 to 1 |
| 6 | 3.15 to 1 | 6.67 to 1 |
| 7 | 2.6 to 1 | 5.57 to 1 |
| 8 | 2.17 to 1 | 4.75 to 1 |
| 9 | 1.86 to 1 | 4.11 to 1 |
| 10 | 1.6 to 1 | 3.6 to 1 |
| 11 | 1.4 to 1 | 3.18 to 1 |
| 12 | 1.22 to 1 | 2.83 to 1 |
| 13 | 1.08 to 1 | 2.54 to 1 |
| 14 | 0.95 to 1 | 2.29 to 1 |
| 15 | 0.85 to 1 | 2.07 to 1 |
| 16 | 0.75 to 1 | 1.88 to 1 |
| 17 | 0.67 to 1 | 1.71 to 1 |
| 18 | 0.6 to 1 | 1.56 to 1 |
| 19 | 0.54 to 1 | 1.42 to 1 |
| 20 | 0.48 to 1 | 1.3 to 1 |
Expand Shrink
When you’re determining your pot odds for the turn and river you determine
them on the turn and then if you don’t hit your draw you determine them again on
the river. This often happens, especially in limit Texas holdem. But if an
opponent moves all in on the turn you simply use the turn and river combined
odds in your decision.
Advanced Texas Holdem Math
Many beginning Texas holdem players look at a discussion about expectation
and instantly decide it’s too hard and ignore it. When they do this they
severely hurt their long term chances at being a profitable player.
We’ve broken down how to look at situations while playing poker in a simple
manner that almost any player can use below. Do yourself a favor and go into
this with an open mind. Once you understand it at a simple level you can learn
more as you gain experience. You may be surprised at just how easy it gets to
determine positive and negative expectation with a little practice.
Expectation
Expectation is what the average outcome will be if you play the same
situation hundreds or thousands of times. Once you determine the expectation you
know if a situation offers positive or negative results on average.
Your goal as a Texas holdem player is to play in as many positive expectation
situations as possible and avoid as many negative expectation situations as
possible.
You need to understand that expectation is something that can be applied to
almost any situation in poker, but it’s also subjective in many areas.
- If you play at a table where every opponent is better than you in the long
run you’re going to lose money. This is a negative expectation situation. - If you play at a table where every opponent is a worse
player than you it’s a positive expectation situation because you’re going to
win in the long run.
The problem is determining whether a situation is positive or negative
expectation when you sit down at a table with some players who are better than
you and some who are worse.
You can find many situations where it’s easier to determine expectation
mathematically, and we’ll teach you how to do this now. While this may seem
overly complicated at first, especially to do at the table while playing, you
don’t need to know exactly how negative or positive a situation is, you only
need to know if it’s positive or negative.
Once you determine if a situation is positive expectation or negative
expectation you simply remember the next time you’re in a similar situation.
Once you start determining expectation you’ll find that you learn mist
situations quickly and only have to think through an occasional situation at the
table.
The best way to see how to determine expectation is by running through a
couple examples.
Example 1
You’re facing a bet after the turn and you have four to a flush.
The pot had $400 in it and your opponent bet $100. You’re certain that if you
miss your flush draw you’ll lose and when you hit your flush draw you’ll win.
In order to see the river you have to call the $100 bet. When you lose you
lose $100, and when you win you get back $600. You get your $100 back plus the
$400 that was in the pot plus the $100 bet your opponent made.
Many players claim that part of the money already in the pot is theirs, but
once you put money into the pot it isn’t yours. The only way to get it back is
to win the pot. So you can’t consider it in any other way when determining
expectation.
The way to see if it’s positive or negative to call is to determine what will
happen on average if you play the same situation many times. Most players find
it easiest to determine by pretending to play the hand 100 times.
In this example you’re going to hit your flush 9 out of 46 times. This means
19.56% of the time you’re going to win and 80.44% of the time you’re going to
lose. To make this simple we’ll round these numbers off to 20% and 80%.
If you have to put $100 in the pot 100 times your total investment is
$10,000. The 80 times you lose you get nothing back. The 20 times you win you
get $600. 20 times $600 is $12,000. When you take the $12,000 you win and
subtract the $10,000 you lose when you play the situation 100 times, you see
that you win $2,000 overall.
To determine how much you win on average per hand simply divide the $2,000 by
100 to get a positive expectation of $20 per hand. This means that every time
you’re in this situation you’ll win on average $20.
The truth is you may win a little more because we’re ignoring the river.
Because you know you can’t win if you miss your flush, you always need to fold on
the river when you miss your draw. Every once in a while you may be able to
extract a small bet from your opponent on the river when you hit your flush,
increasing your average expectation. Sometimes it’s even correct for your
opponent to call on the river in this situation. See the next example to see
why.
Example 2
Let’s say you’re playing the same hand as above but you have a
straight and your opponent appears to be drawing to a flush. You’re on the
river, the pot has $600 in it, and the board has the third suited card hit on the
river.
If your opponent was drawing to the flush, they completed it and you’re going
to lose the hand. In this situation your opponent bets $20.
In this situation you clearly have to call.
The reason you have to call is because you can’t know for certain your
opponent was drawing to the flush. They may be bluffing or have two pair or any
other number of hands that aren’t as good as your straight.
Let’s look at the math behind this decision.
If you play the situation 100 times your total investment is $20 times 100,
or $2,000.
When you win you get $640, consisting of the original $600 pot, your
opponent’s $20 bet, and your $20 call. If you win three hands you get back
$1,920 for a loss of $80, or 80 cents per hand.
If you win at least four times you’re in a positive expectation situation.
Four wins nets $2,560 for an overall win of $560, or $5.60 per hand.
What this means is if your opponent is bluffing or has a weaker hand just
four times out of 100 or more, calling is a positive expectation situation. Four
times out of 100 is only 4%. You’ll win at least 4% of the time in this
situation.
The numbers get closer the more your opponent bets on the river, and the
closer the numbers get the more you’re going to need to use what you know about
your opponent to determine if a situation is positive or not.
Start looking at every decision you make at the Texas holdem tables in terms
of positive and negative expectation.It’s hard at first, but the more you
practice the better you’ll get at predicting if a situation offers positive
expectation.
Summary
Texas holdem math is often the only thing that separates winning and losing
players. Take the time to learn the basics now so you can improve your game in
every way possible as you gain experience. This guide is the perfect place to
start for players of every experience level.
Table Of Contents
If you want to learn how to play Texas hold'em games, then you need to start from the basic rules and hands. That's exactly what you'll find on this beginner's guide to the game.
Texas hold'em is a simple poker game, but it can be daunting to get to grips with.

But don't let that put you off. By the time you are down with this beginner's guide to Texas hold'em, you will know:
1. What Is Texas Hold'em Poker?
Texas Hold'em is the most popular of all poker variations.
All of the marquee tournaments around the world (including those played at the World Series of Poker, the World Poker Tour, the and the European Poker Tour) feature the no-limit variation of this game.
Texas hold'em is so popular that is the only poker game many players will ever learn.
It takes a moment to learn, but a lifetime to master.
Discovering how to play Texas hold'em poker is not difficult and the simplicity of its rules, gameplay, and hand-ranking all contribute to the popularity of the game.
However, don't let the simplicity of the game mislead you.
The number of possible situations and combinations is so vast that Texas hold'em can be an extremely complex game when you play at the highest levels.
If you are approaching the game of Texas hold'em for the first time, starting from the basic rules of the game is key. Not only these are the easiest ones to learn, but they are also essential to understand the gameplay and, later on, the game's basic strategy.
Want to Practice Poker Online?These are the best sites to play free games of Texas hold'em online. Use your e-mail address to register and sit at the free tables to play!
'>2. Texas Hold'em Rules
So how do you play Texas hold'em?
The goal of a Texas hold'em game is to use your hole card and in combination with the community cards to make the best possible five-card poker hand.
Hold'em is not unlike other poker games like five-card draw.
However, the way players construct their hands in Texas hold'em is a little different than in draw poker.
It's always possible a player can 'bluff' and get others to fold better hands.
- In a game of Texas hold'em, each player is dealt two cards face down (the 'hole cards')
- Throughout several betting rounds, five more cards are (eventually) dealt face up in the middle of the table
- These face-up cards are called the 'community cards.' Each player is free to use the community cards in combination with their hole cards to build a five-card poker hand.
While we will see each betting round and different phase that forms a full hand of a Texas hold'em game, you should know that the five community cards are dealt in three stages:
- The Flop: the first three community cards.
- The Turn: the fourth community card.
- The River:The fifth and final community card.
Your mission is to construct your five-card poker hands using the best available five cards out of the seven total cards (the two hole cards and the five community cards).
You can do that by using both your hole cards in combination with three community cards, one hole card in combination with four community cards, or no hole cards.
If the cards on the table lead to a better combination, you can also play all five community cards and forget about yours.
In a game of Texas hold'em you can do whatever works to make the best five-card hand.
If the betting causes all but one player to fold, the lone remaining player wins the pot without having to show any cards.
For that reason, players don't always have to hold the best hand to win the pot. It's always possible a player can 'bluff' and get others to fold better hands.
READ ALSO: Common Poker Tells: How to Read People in Poker
If two or more players make it all of the way to the showdown after the last community card is dealt and all betting is complete, the only way to win the pot is to have the highest-ranking five-card poker hand.
Now that you know the basics of Texas hold'em and you start to begin gaining an understanding of how the game works, it's time to get into some specifics.
These include how to deal Texas hold'em and how the betting works.
Basic Rules Key Takeaways:
- A game of Texas hold'em feature several betting rounds
- Players get two private and up to five community cards
- Unless all players abandon the game before the showdown, you need the highest poker hand to win
How to Play
Let's have a look at all the different key aspects of a Texas hold'em game, including the different positions at the table and the betting rounds featured in the game.
The Button
The play moves clockwise around the table, starting with action to the left of the dealer button.
The 'button' is a round disc that sits in front of a player and is rotated one seat to the left every hand.
When playing in casinos and poker rooms, the player with the dealer button doesn't deal the cards (the poker room hires someone to do that).
In when you play poker home games with friends the player with the button usually deals the hands.
The button determines which player at the table is the acting dealer.
The first two players sitting to the immediate left of the button are required to post a 'small blind' and a 'big blind' to initiate the betting.
From there, the action occurs on multiple streets:
How To Learn Texas Holdem Odds Poker
- Preflop
- Flop
- Turn
- River
Each one of these moments (or 'streets' in the game's lingo) is explained further below.
The button determines which player at the table is the acting dealer.
In Texas hold'em, the player on button, or last active player closest to the button receives the last action on all post-flop streets of play.
While the dealer button dictates which players have to post the small and big blinds, it also determines where the dealing of the cards begin.
The player to the immediate left of the dealer button in the small blind receives the first card and then the dealer pitches cards around the table in a clockwise motion from player to player until each has received two starting cards.
READ ALSO: Poker Positions Explained: the Importance of Position in Poker
The Blinds
Before every new hand begins, two players at the table are obligated to post small and big blinds.
The blinds are forced bets that begin the wagering.
Without these blinds, the game would be very boring because no one would be required to put any money into the pot and players could just wait around until they are dealt pocket aces (AA) and only play then.
The blinds ensure there will be some level of 'action' on every hand.
In tournaments, the blinds are raised at regular intervals. In cash games, the blinds always stay the same.
In tournaments, the blinds are raised at regular intervals.
- As the number of players keeps decreasing and the stacks of the remaining players keep getting bigger, it is a necessity that the blinds keep increasing throughout a tournament. [*]In cash games, the blinds always stay the same.
The player directly to the left of the button posts the small blind, and the player to his or her direct left posts the big blind.
The small blind is generally half the amount of the big blind, although this stipulation varies from room to room and can also be dependent on the game being played.
In a '$1/$2' Texas holdem game, the small blind is $1 and the big blind is $2.
First Betting Round: Preflop
The first round of betting takes place right after each player has been dealt two hole cards.
The first player to act is the player to the left of the big blind.
This position referred to as 'under the gun' because the player has to act first. The first player has three options:
- Call: match the amount of the big blind
- Raise: increase the bet within the specific limits of the game
- Fold: throw the hand away
If the player chooses to fold, he or she is out of the game and no longer eligible to win the current hand.
Players can bet anywhere from the amount of the big blind (the minimum bet allowed) up to the total amount in the current pot.
The amount a player can raise to depends on the game that is being played.
In a game of no-limit Texas hold'em, the minimum opening raise must be at least twice the big blind, and the maximum raise can be all of the chips a player has in his or her stack (an 'all-in' bet).
There are other betting variations in hold'em poker.
In fixed-limit hold'em (or just 'limit hold'em), a raise is always exactly twice the big blind.
In pot-limit hold'em (played much less often than the other variations), players can bet anywhere from the amount of the big blind (the minimum bet allowed) up to the total amount in the current pot.
After the first player ('under the gun') acts, the play proceeds in a clockwise fashion around the table with each player also having the same three options — to call, to raise, or fold.
Once the last bet is called and the action is 'closed,' the preflop round is over and play moves on to the 'flop.'
Texas Holdem Odds Chart
Second Betting Round: The Flop
After the first preflop betting round has been completed, the first three community cards are dealt and a second betting round follows involving only the players who have not folded already.
A check simply means to pass the action to the next player in the hand.
In this betting round (and subsequent ones), the action starts with the first active player to the left of the button.
Learn Texas Holdem Free
Along with the options to bet, call, fold, or raise, a player now has the option to 'check' if no betting action has occurred beforehand.
A check simply means to pass the action to the next player in the hand.
Again betting continues until the last bet or raise has been called (which closes the action).
It also can happen that every player simply chooses not to be and checks around the table, which also ends the betting round.
Third Betting Round: The Turn
Call – match the amount of the big blind
The fourth community card, called the turn, is dealt face-up following all betting action on the flop.
Once this has been completed, another round of betting occurs, similar to that on the previous street of play.
Again players have the option to options to check, bet, call, fold, or raise.
Final Betting Round: The River
Fold – throw the hand away
The fifth community card, called the river, is dealt face-up following all betting action on the turn.
Once this has been completed, another round of betting occurs, similar to what took play on the previous street of play.
Once more the remaining players have the option to options to check, bet, call, fold, or raise.
After all betting action has been completed, the remaining players in the hand with hole cards now expose their holdings to determine a winner. This is called the showdown.
The Showdown
Players construct their hands by choosing the five best cards from the seven available
The remaining players show their hole cards, and with the assistance of the dealer, a winning hand is determined.
The player with the best combination of five cards wins the pot according to the official poker hand rankings.
3. The Hands in Texas Hold'em
These hand rankings aren't specifically part of Texas hold'em rules, but apply to many different poker games.
- Royal Flush — five cards of the same suit, ranked ace through ten; e.g., A♥K♥Q♥J♥10♥
- Straight Flush — five cards of the same suit and consecutively ranked; e.g., 9♣8♣7♣6♣5♣
- Four of a Kind — four cards of the same rank; e.g., Q♣Q♥Q♦Q♠4♦
- Full House — three cards of the same rank and two more cards of the same rank; e.g., J♣J♥J♠8♦8♥
- Flush — any five cards of the same suit; e.g., A♠J♠8♠5♠2♠
- Straight — any five cards consecutively ranked; e.g., Q♣J♦10♥9♠8♦
- Three of a Kind — three cards of the same rank; e.g., 8♣8♠8♦K♣4♥
- Two Pair — two cards of the same rank and two more cards of the same rank; e.g., A♠A♣J♦J♣7♠
- One Pair — two cards of the same rank; e.g., 10♥10♣9♥4♦2♦
- High Card — five unmatched cards; e.g., A♣J♦10♠5♣2♥ would be called 'ace-high'
Players construct their hands by choosing the five best cards from the seven available (their two hole cards and the five community cards).
If the board is showing 9♣5♠K♦3♠A♥, a player with the two hole cards 9♠ would have two pair (aces and nines) and would lose to a player who has 9♦9♥ for three of a kind (three nines).
Learning hold'em poker begins with understanding how hands are dealt and the order of play as described above.
Of course, learning Texas hold'em rules is just the beginning, as the next step is to learn strategy which involves understanding what constitutes good starting hand selection, the odds and probabilities associated with the game, the significance of position and getting to act last during those post-flop betting rounds, and many other aspects of the game.
4. How to Play Texas Hold'em Games Online
Now that you know how Texas Hold'em works, it's time to put the theory into practice and play your first games.
The best way to start playing Texas Hold'em is to start from these free poker games available online and then move up to the real money action only when you feel comfortable enough to do so.
All the 'must-have poker rooms' below offer free games to practice online.
If you are completely new to the game, you should go for play money options, first. These risk-free games with fake money are an excellent way to familiarise with the different moments of play and the betting rounds.
The play money games are a great way to learn more about the hand rankings and begin to read the board fast enough to take all the right decisions at the right time.
After that, you should more to the poker freerolls. These are free poker tournaments with actual prizes on tap that range from free money to free entries into more expensive real money games.
Must Have Rooms
Home to the biggest tournaments online, these rooms also have the largest player base, great bonuses, tons of action and the best software. If you don't have accounts here, you are missing out on the best that online poker has to offer.
PartyPokerplatinum
Up to $30 of Free Play
RATING
9.9 ★
Key features
- Excellent mobile poker games
- Lots of free and real-money action
- One of the most trusted brands in online gaming